Mitosis is the process of cell division in which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells, hence called equational division. This process is divided into four stages of nuclear division (karyokinesis).
1) Prophase
2) Metaphase
3) Anaphase
4) Telophase
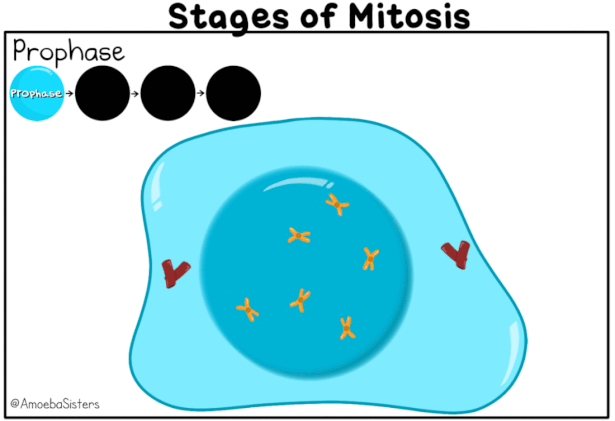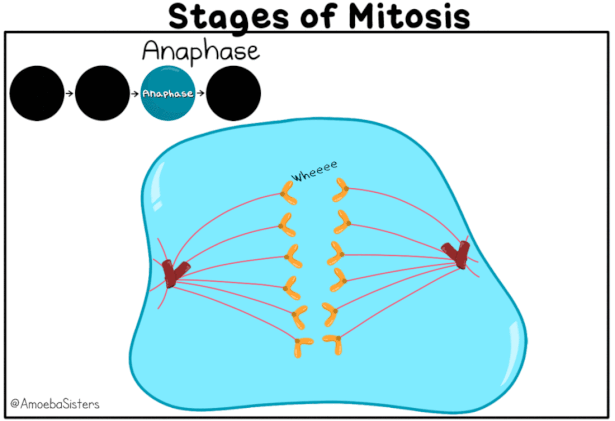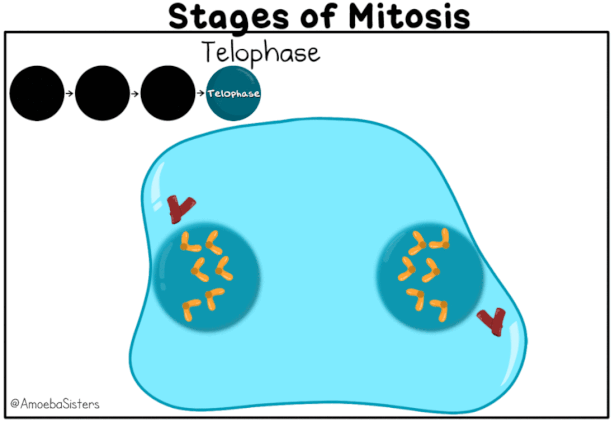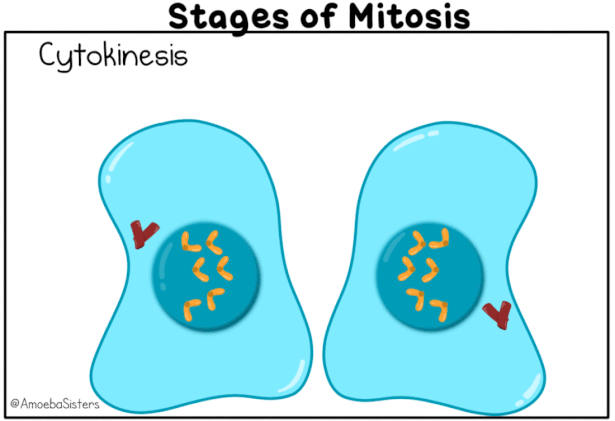
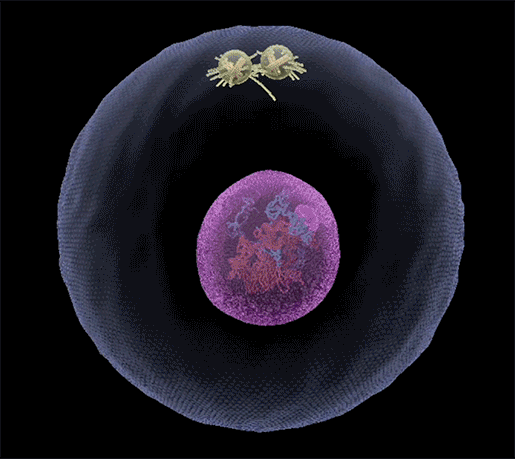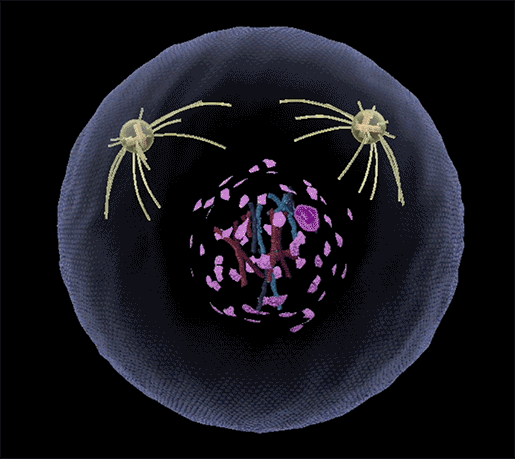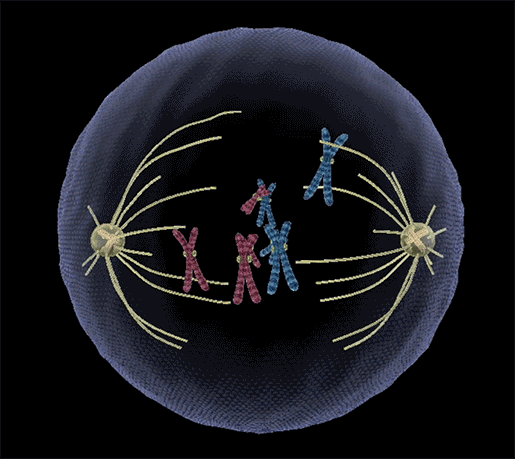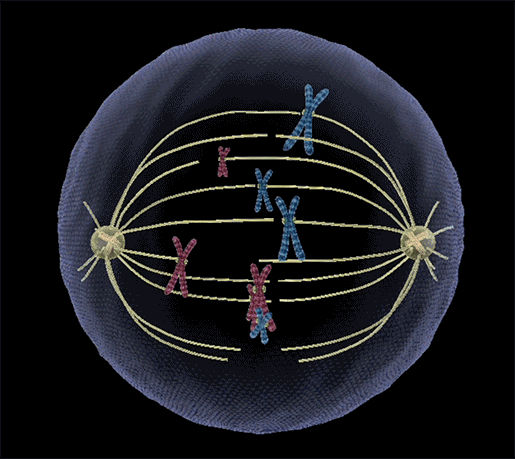
Prophase:
- This is the first stage of karyokinesis of mitosis.
- Prophase is marked by the initiation of condensation of chromosomal material (which becomes visible under a microscope).
- The centrosome moves towards opposite poles of the cell. Chromosomes are seen to be composed of two chromatids attached together at the centromere.
- Each centrosome radiates out microtubules called asters. The two asters together with spindle fibers form mitotic apparatus.
- Cells at the end of prophase, when viewed under the microscope, do not show Golgi complexes, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus and the nuclear envelope.
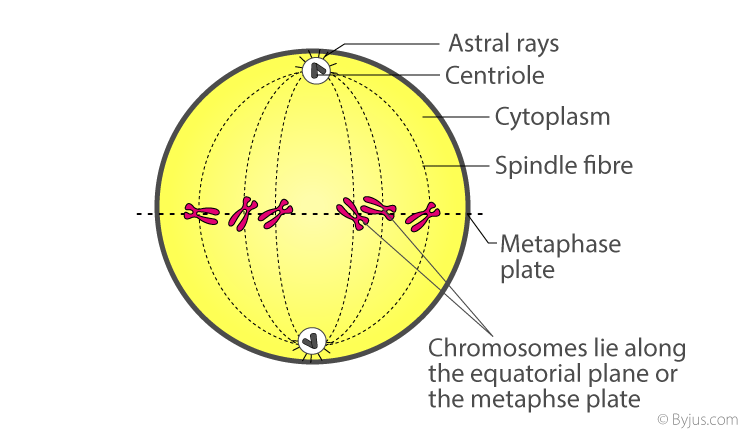
Metaphase:
- The complete disintegration of the nuclear envelope marks the start of the metaphase.
- Chromosomes are highly condensed in this stage, because of that we can clearly observe the structure and morphology of chromosomes under a microscope.
- During metaphase, the chromosomes align along the equator of the cell (The plane of alignment of the chromosomes at metaphase is referred to as the metaphase plate). This is also called Congression.
- Congression: Arrangement of all chromosomes at equatorial plate/metaphasic plate.
- The spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes and prepare to pull them apart.
- Spindle fibers attach to kinetochores of chromosomes.
- Chromosomes are moved to spindle equator and get aligned along metaphase plate through spindle fibers to both poles.
- During anaphase, the spindle fibers shorten and pull the sister chromatids apart
- Centromeres split and chromatids separate.
- Chromatids move to opposite poles.
- Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles and their identity is lost as discrete (seperate) elements.
- Nuclear envelope develops around the chromosome clusters at each pole forming two daughter nuclei.
- Nucleolus, Golgi complex and ER reform.
Cytokinesis: (Cytoplasmic division)
This is the final stage of the cell division, the cytoplasm of the cell divides, resulting in the formation of two daughter cells.
In an animal cell, this is achieved by the appearance of a furrow in the plasma membrane. The furrow gradually deepens and ultimately joins in the center dividing the cell cytoplasm into two (Contractile ring composed of actin and myosin filaments forms around the cell, pinching the cell in two).
- Cytokinesis occurs differently due to the presence of cell wall. Instead of cleavage, a cell plate forms in the center of the cell, dividing the cytoplasm into two separate compartments.
- The cell plate gradually develops into a new cell wall that separates the two daughter cells (cell wall represents the middle lamella between the walls of two adjacent cells).
- At the time of cytokinesis, organelles like mitochondria and plastids get distributed between the two daughter cells.
In some organisms karyokinesis is not followed by cytokines as a result of which multinucleate condition arises leading to the formation of syncytium (Ex: Liquid endosperm in coconut).
Importance of Mitosis:
It allows the cells to divide, grow, repair and reproduce and is essential for the survival and functioning of all living organisms.
Extra points:
- Kinetochores: Small disc-shaped structures at the surface of the centromeres, these structures serve as the sites of attachment of spindle fibers to the chromosomes.
- Cytokinesis is an essential process for the growth, development and repair of multicellular organisms, as well as for the replication of unicellular organisms. Defects in cytokinesis can lead to abnormal cell division and contribute to the development of diseases, including cancer.
- In animal cells cytokinesis is by cell furrow formation and in plants it is by cell plate formation.
- Phragmoplast is responsible for the formation of cell-plate in plant cells during cytokinesis.








No comments:
Post a Comment